Basic HTML Version




Molecular Plant Breeding 2011, Vol.2, No.14, 98
-
100
http://mpb.sophiapublisher.com
100
electrophoresis) is the best and easiest way to identify
the differentially expressed proteins, by comparing the
2D gel profiles of proteins extracted from plant
samples (Si
+
and Si
-
). Once we have these profiles, we
can easily locate the proteins whose expression is
enhanced as well as reduced due to application of Si.
An alternative approach can be 1D shotgun
proteomics analysis using tandem mass spectrometry
(LC-MS/MS). By means of MS these proteins can be
identified and their functionality can be determined
using various bioinformatics tools and such proteins
can be assigned to various metabolic pathways. As
such it will help us in understanding the actual impact
of Si on various metaboltic pathway which may
unlock the secret of potential versatility of this
micronutrient and will help us in fully exploring the
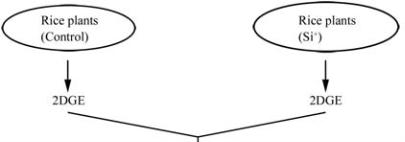
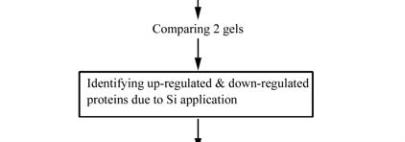
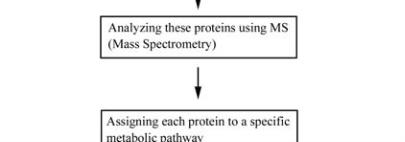
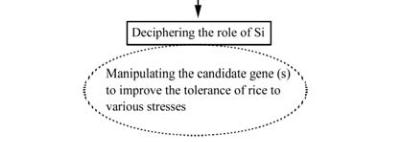
potential of Si. The strategy is explained in Figure 2.
Figure 2 Proteomics based approach to decipher the role of Si
in giving tolerance to various stresses
Author Contributions
SMZ and MN wrote the paper, GKA and RR also read the manuscript and
revised it. All authors had read and consented the final text.
Acknowledgements
SMZ is grateful to the Vice Chancellor, SKUAST-J (Dr. B. Mishra) for
providing necessary facilities.
References
Bond R., and McAuliffe J.C., 2003, Silicon Biotechnology: New opportunities
for carbohydrate science, Aust. J. Chem., 56(1): 7-11 doi:10.1071/CH0
2224
Bouman B.A.M., and Tuong T. P., 2001, Field water management to save
water and increase its productivity in irrigated rice, Agricultural Water
Management, 49(1): 11-30 doi:10.1016/S0378-3774(00)00128-1
Epstein E., 1994, The anamoly of silicon in plant biology, Proc. Natl. Acad.
Sci. USA, 91(1): 11-17 doi:10.1073/pnas.91.1.11
Epstein E., 2001, Silicon in Plants: Facts vs Concepts, In: Datnoff L.E.,
Synder G.H., and Korndorfer G.H. eds., Silicon in Agriculture, Elsevier
Science, Amsterdam, pp.1-15 doi:10.1016/S0928-3420(01)8 0005-7
Fawe A., Menzies J.G., Cherif M., and Belanger R.R., 2001, Silicon and
disease resistance in dicotyledons, In: Datnoff L.E., Synder G.H., and
Korndorfer G.H. eds., Silicon in Agriculture, Elsevier Science,
Amsterdam, pp.159-169 doi:10.1016/S0928-3420(01)80013-6
Gascho G.J., 2001, Silicon sources for agriculture, In: Datnoff L.E., Synder
G.H., and Korndorfer G.H. eds., Silicon in Agriculture, Elsevier
Science, Amsterdam, pp.197-199 doi:10.1016/S0928-3420(01)80016-1
Marschner H., ed., 1995, Mineral nutrition of higher plants, Academic Press,
London, pp.1-889
Ma J.F., Higashitani A., Sato K. and Takeda K., 2002, Genotypic variation
in Silicon concentration of barley grains, Plant and soil, 249(2):
383-387
Ma J.F., Miltani N., Nagao S., Konishi S., Tamai K., Iwashita T. and Yano
M., 2004, Characterization of the silicon uptake system and molecular
mapping of the silicon transporter gene in rice, Plant Physiol., 136(2):
3284-3289 doi:10.1104/pp.104.047365 PMid:15448199 PMCid:523387
Ma J.F., Tamai K., Yamaji N., Mitani N., Konishi S., Katsuhara M., Ishiguro
M., Murata Y., and Yano M., 2006, A silicon transporter in rice, Nature,
440(7084): 688-691 doi:10.1038/nature04590 PMid:16572174
Nwugo C.C., and Huerta A.J., 2008, Silicon-induced cadmium resistance in
rice (
Oryza sativa
), J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci., 171(6): 841-848 doi:10.100
2/jpln.200800082
Zargar S.M., Nazir M., Agrawal G.K., Kim D.W., and Rakwal R., 2010,
Silicon in plant tolerance against environmental stressors: Towards
crop improvement using Omics approaches, Current Proteomics, 7(2):
135-143 doi:10.2174/157016410791330507

