Basic HTML Version


Molecular Plant Breeding 2010, Vol.1 No.2
http://mpb.sophiapublisher.com
Page 2 of 5
the first generation of
Bt
gene,
cry1Ac
got good
performance at the toxicity to the target pests, the
contents of toxin protein got 11.09±0.35 µg/g leaf
fresh weight, and possessed an overall soluble protein
content of 0.02%. While
cry2A*
and
cry1C*
are
considered as the second generation of
Bt
gene, the
contents of their toxin protein separately reached
84.94±2.34 and 1.46±0.12 μg/g leaf fresh weight(Tang
et al., 2006; Chen et al., 2005). They not only have
severe toxicity to the target pests, but also have better
target specificity to the pests without expressing high
dose of the toxin protein, which would lower the
burden of plant. Therefore, these Bt genes mentioned
above have got excellent performances to the
resistance. What’s more, the expression of the Bt toxin
has extreme specificity in plants, only in the leaves
and stems could the toxin protein be efficiently
expressed, while in the seeds, the expression of Bt
protein nearly could not be found even that using
real-time to detect them. So the above three
Bt
genes
are safe to be used in the application in the future.
In the 1950s, Bt insecticides as biopesticides became
popular in America (Martin and Travers, 1989), and
there were 182 sorts of Bt reagents which were
registered in US Environmental Protection Agency
(EPA) until 1995. In 1987, the first
Bt
transgenic plant
was reported (Barton et al., 1987; Fischhoff et al., 1987;
Vaeck et al., 1987). In 1995, the Bt transgenic plants got
the commercialization for the first time in Canada. In
2004, the global area of
Bt
crops got 2240 hectare(James,
2004). Huazhong Agricultural University got the first
safety certificate of cry1Ab/c transgenic crops, Huahui
No.1 and Bt Shanyou 63. In this study, the three genes,
cry1Ac
,
cry1C*
and
cry2A*
, were introgressed to 9311
and Fuhui 838 from the donor parents respectively by
molecular maker selection approach in order to supply
the useful materials and potential theory basis for the
application of
Bt
crops in the future.
1 Results
1.1 Homozygous lines identified by marker-assisted
selection
All the three
Bt
genes were incorporated with bar genes
which could be used as weedicide. The designed
markers for homozygous line selection are dominant in
this study. Therefore, both marker-assisted selection
and assay of weedicide were used to get the
homozygous lines. Only when all the 24 plants were
positive by PCR detection and were resistant to the
weedicide could we take them as one homozygous line.
In this study, more than two homozygous lines with
each
Bt
gene were found by the above ways. The part
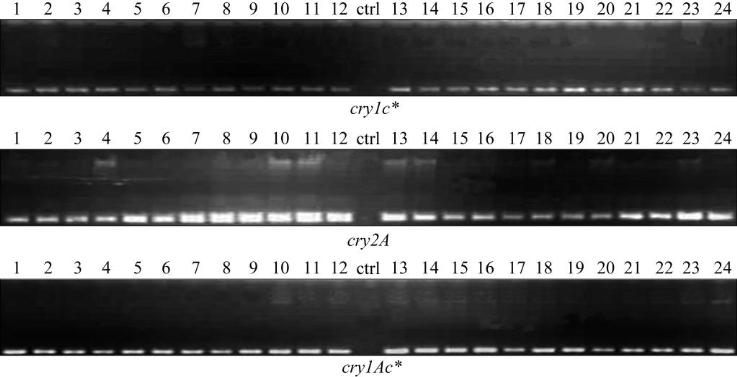
PCR detection figures of homozygous lines are as
follows (Figure 1).
Figure 1 PCR detection results of
cry1C*, cry2A*
and
cry 1Ac
homozygous lines
Note: 1~24 are homozygous individuals and the control was in the middle

